Introduction
What is Plasma Cutting?
Plasma cutting is a quick and accurate process used for cutting conductive materials (metals) by forcing a concentrated stream of ionized plasma through a given workpiece. The plasma cutting process evolved from plasma welding in the 1960’s, and has since become an industrial staple replacing the slower and less refined oxyfuel process.
Today, plasma cutters come in all shapes and sizes; ranging from large industrial machines down to hobby-level plasma cutters that are similar in power output and size to a common home welder. Most hobby-level plasma cutters are supplied with a hand torch that can quickly be moved across the surface of a metal plate to produce a desired cut. Typically all that is required to run one of these plasma cutters is a basic source of shop air (air compressor) and power input (some plasma cutters are even capable of running on either 120V or 220V).
With the recent availability of these low cost and easy-to- use plasma cutters, the process has become increasingly more popular among home builders and hobbyists alike.

CNC Plasma Cutting
The biggest limitation to hand-held plasma cutting is that an operator is required to have a high skill level in order to make clean and accurate cuts on complex geometry. Even the most talented plasma torch operators would struggle to replicate machine quality parts with high repeatability. With the emergence of Computer Numerically Controlled (CNC) technology, machines were created that utilized a plasma cutting torch to produce high quality parts with incredible speed and accuracy.
The process of CNC plasma cutting involves the electromechanically controlled movement of a CNC cutting torch along a pre-programmed tool path. The system is comprised of a plasma cutter, torch (either machine or hand-held), motion controller, electromechanical drive system, and a cutting surface. Parts are first designed in a two-dimensional CAD software and then tool-paths are generated from the part geometry in a CAM software. The CAM software creates a numeric ‘G code’ that can be uploaded to the CNC plasma machines motion controller which then translates this code to execute the desired cut. Given the complex nature of CNC plasma cutting, the process has been largely reserved for industrial uses only.
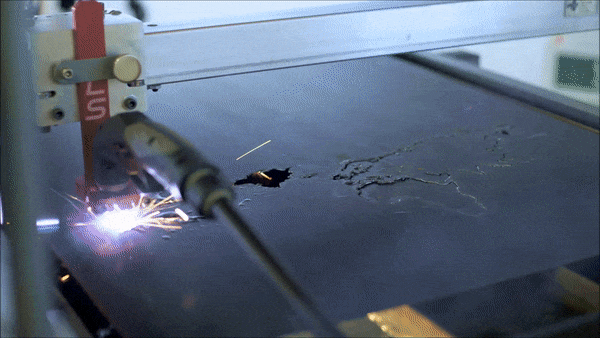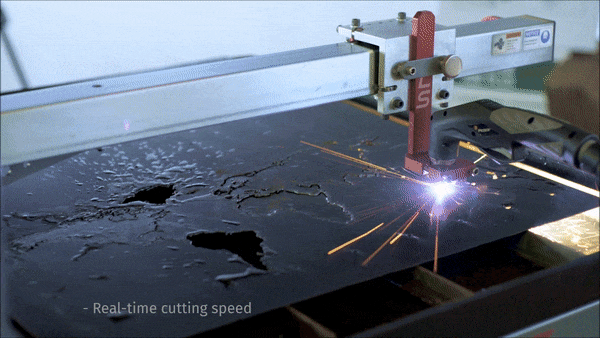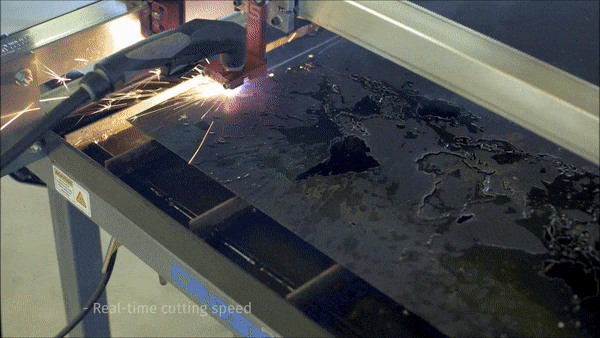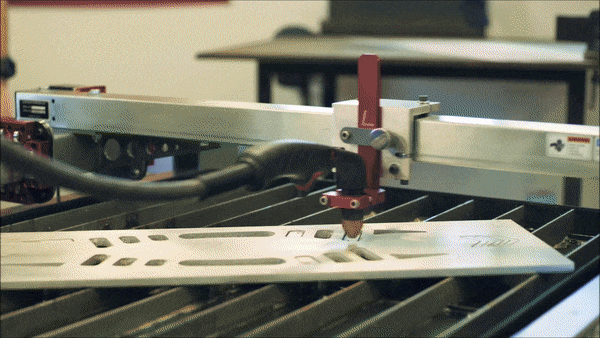
Langmuir Systems CrossFire™
The Langmuir Systems CrossFire™ CNC plasma cutting machine was the response to a simple question: How can CNC plasma cutting be adapted to the hobby level while still producing part quality comparable to expensive industrial machinery?
As a company we found that the process of CNC plasma cutting was exclusively restricted to the industrial sector because these machines were priced outside of what the average home maker could afford. The engineering team here at Langmuir Systems spent the next two years benchmarking the industry in an attempt to understand the key components of high-end CNC plasma cutting machinery. By stripping down these machines to their most basic form, we were able to re-construct the CNC plasma table from the ground up.
What resulted was the creation of the industry’s first affordable CNC plasma cutting machine capable of producing equivalent part quality at a fraction of the price. Here at Langmuir Systems we are dedicated to putting high-end machinery into the hands of everyday people and we are confident that the CrossFire™ CNC plasma machine is our first step towards achieving this goal.
